Specification of health data transfer from devices to DiGA (§ 374a SGB V)
Seiteninhalt:
Medical aids and implants often can measure various kinds of data, depending from the kind of device and the concrete product. Not all of this data can be considered by mid 2027 when § 347a SGB V comes into effect. Therefore an assessment on typical use cases within prioritized domains was conducted in order to discover the kinds of data that are especially relevant for care scenarios which can be supported by DIGA (see chapter on Methodology).
This page lists these Mandatory Interoperable Values (MIVs) for the domains that have been assessed so far.
Self-management tools used by patients to determine glucose levels analyze either capillary blood (“bloody measurement” on the fingertip) or interstitial fluid (e.g. measurements performed through real-time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (rtCGM)). Other measurement methods - e.g. using aterial blood - are primarily used in the doctor’s office and are not taken into account for the HDDT Usecase “Diabetes Self-Management”.
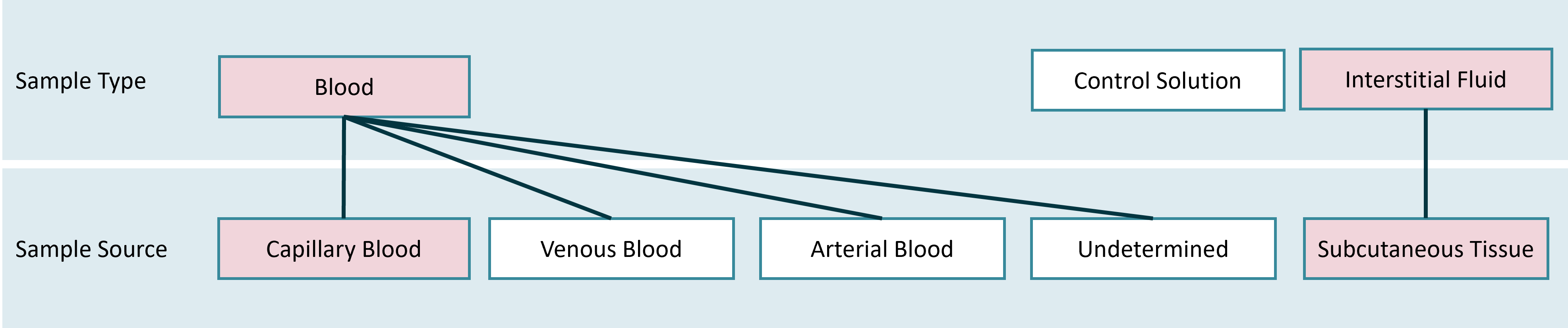
For the initial specification (version 1) of HDDT, two mandatory interoperable values (MIVs) are defined for diabetes self-management:
The table below lists typical use cases and certification relevant systems for these MIVs.
| MIV | examples of typical use cases | examples of certification relevant systems |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Glucose Measurement | • monitoring of patients with a combination of basal insulin with oral antidiabetic drugs • diabetes diary for DMT2 patients |
• blood glucose meter (glucometer) |
| Continuous Glucose Measurement | • supporting patients in flattening glucose curves • analyzing behavioral effects on glucose level • gathering key metrics for measuring the status of the diabetes therapy • analyzing hidden hypoglycaemias |
• real-time Contiuous Clucose Monitoring (rtCGM) • Closed Loop Systems |
The MIV Blood Glucose Measurement covers values from “bloody measurements” using capillary blood from the finger tip. Measurements are performed based on a care plan (e.g. measuring blood sugar before each meal) or ad hoc (e.g. a patient feeling dim what may be an indicator for a hypoglycamia). Values are very acurate and therefore best suited for therapeutical decision making.
| Defining ValueSet | The MIV Blood Glucose Measurement is defined by the FHIR ValueSet Blood Glucose Measurement from LOINC. This ValueSet contains LOINC codes for blood glucose measurements using blood or plasma as reference methods with the values provided as mass/volume and moles/volume. In addition more granular LOINC codes for “Glucose in Capillary blood by Glucometer” provided as mass/volume and moles/volume are included with the value set because these codes are already in use by several manufacturers of glucometers. |
| SMART Scopes | patient/Observation.rs?code:in=https://gematik.de/fhir/hddt/ValueSet/hddt-miv-blood-glucose-measurement patient/Device.rs patient/DeviceMetric.rs |
| FHIR Observation Profile | Device Data Recorders provide Blood Glucose Measurement to DiGA using the MIV-specific Observation Profile HDDT Blood Glucose Measurement. This profile allows to capture a single blood glucose value as a FHIR Observation resource. |
| FHIR Interactions | Access to the ressources is given through standard FHIR read and search RESTful interactions as described in the MIV-specific API. |
| Aggregated Data | By now there are no aggregated data defined for the MIV “Blood Glucose Measurement”. |
| Vendor Holdup | The maximum acceptable delay between data availability in the Health Record and data availability through the HDDT interface is 60 seconds. |
Historic-Data-Period |
Device Data Recorders that provide Blood Glucose Measurement data MUST make the measured values retrievable for at least 30 days. |
Grace-Period |
A Device Data Recorder MAY reject a DiGA’s request for a patient’s Blood Glucose Measurement if the previous request for that patient was answered less than 15 minutes ago. |
Chunk-Time-Span |
not applicable |
The MIV Continuous Glucose Measurement covers values from continuous monitoring of the glucose level, e.g. by rtCGM in interstitial fluid (ISF). Measurements are performed through sensors with a sample rate of up to one value per minute. By this Continuous Glucose Measurement can e.g. be used to assess dependencies between a patient’s individual habits and behaviours and his glucose level. Due to the high density of values over a long period of time, many key metrics can be calculated from Continuous Glucose Measurement which help the patient and his doctor to easily capture the status of the patient’s health and therapy.
| Defining ValueSet | The MIV Continuous Glucose Measurement is defined by the FHIR ValueSet Continuous Glucose Measurement from LOINC. This ValueSet includes codes relevant to continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) of ISF glucose, considering mass/volume and moles/volume as commonly used units. In the future codes defining non-invasive glucose measuring methods may be added to this value set. |
| SMART Scopes | patient/Observation.rs?code:in=https://gematik.de/fhir/hddt/ValueSet/hddt-miv-continuous-glucose-measurement patient/Device.rs patient/DeviceMetric.rs |
| FHIR Observation Profile | Device Data Recorders provide Continuous Glucose Measurement to DiGA using the MIV-specific Observation Profile HDDT Continuous Glucose Measurement. This profile allows to share sampled glucose values as FHIR Observation resources. Each resource holds multiple values while the time stamp of each value can be determined by the time stamp of the first value and the fixed sample rate. |
| FHIR Interactions | Access to the ressources is given through standard FHIR read and search RESTful interactions as described in the MIV-specific API. |
| Aggregated Data | As stated above, Continuous Glucose Measurement sampled data are a basis for many key metrics used in diabetes therapy monitoring, e.g. times in ranges (e.g. times in hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia) and Glucose Management Index (GMI). Device Data Recorders MUST provide the structured, coded part of the HL7 CGM Summary Report to DiGA using the MIV-specific Profile HDDT CGM Summary Report. This profile allows to share a well defined set of relevant key metrics as FHIR Observation resources. Access to the summary report is provided through the FHIR operation $hddt-cgm-summary. |
| Vendor Holdup | The maximum acceptable delay between data availability in the Health Record and data availability through the HDDT interface is 15 minutes. |
Historic-Data-Period |
Device Data Recorders that provide Continuous Glucose Measurement data MUST make the measured values and aggregated key metrics (per CGM Summary Report) retrievable for at least 30 days. |
Grace-Period |
A Device Data Recorder MAY reject a DiGA’s request for a patient’s Continuous Glucose Measurement if the previous request for that patient was answered less than 15 minutes ago. |
Chunk-Time-Span |
The Chunk-Time-Span depends on the sample rate of the personal health device. Chunks of sampled data SHOULD be sized to hold between 200 and 2000 single data points. |
MIVS for this domain are expected to be published by November 2025.
MIVS for this domain are expected to be published by November 2025.